Microscopic anatomy of tissues
Deformation mechanisms in soft biological tissues often depend on density and configuration of collagen fibers. Other extracellular matrix components contribute determining the elastic and dissipative deformation behavior. Physically based models are formulated using information related to the distribution of fibers, mechanisms of reorientation, cross-link density, connectivity, fibers bending and tensile stiffness, and interaction with a matrix.
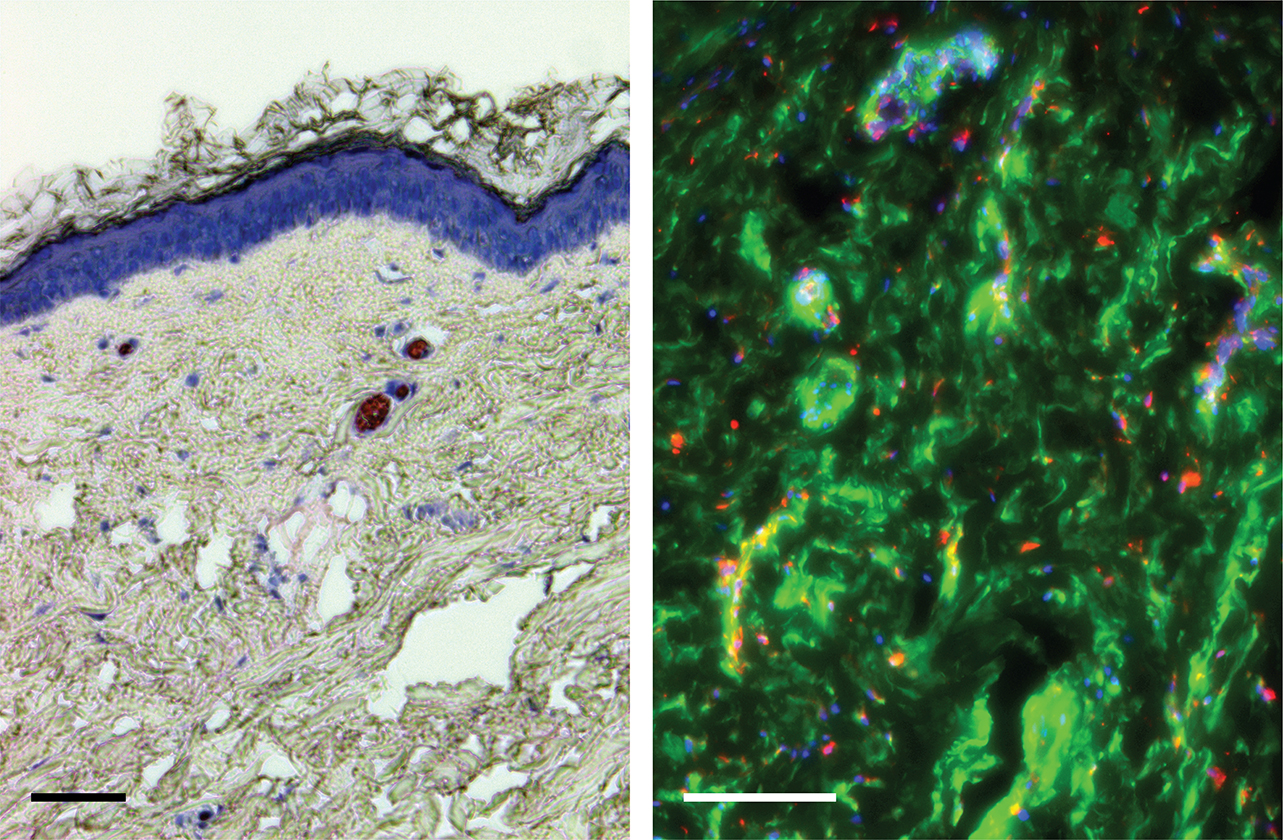
We combine mechanical characterizations with histology and immunofluorescence, techniques aimed at studying the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues [1-5].
[1] Ehret A.E., Bircher K., Stracuzzi A., Marina V., Zündel M., Mazza E. (2017) Inverse poroelasticity as a fundamental mechanism in biomechanics and mechanobiology. Nat. Commun. 8, 1002. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00801-3
[2] Pensalfini M., Haertel E., Hopf R., Wietecha M., Werner S., Mazza E. (2018) The mechanical fingerprint of murine excisional wounds. Acta Biomater. 65, 226-236. DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.10.021.
[3] Bircher K., Zündel M., Pensalfini M., Ehret A.E., Mazza E. (2019) Tear resistance of soft collagenous tissues. Nat. Commun. 10, 792. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-08723-y.
[4] Wietecha M.S., Pensalfini M., Cangkrama M., Müller B., Jin J., Brinckmann J., Mazza E., Werner S. (2020) Activin-mediated alterations of the fibroblast transcriptome and matrisome control the biomechanical properties of skin wounds. Nat. Commun. 11, 2604. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16409-z.
[5] Pensalfini M., Ehret A.E., Stüdeli S., Marino D., Kaech A., Reichmann E., Mazza E. (2016) Factors affecting the mechanical behavior of collagen hydrogels for skin tissue engineering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 69, 85-97. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2016.12.004.